【diffusers】(三) pipeline原理及自定义训练推理-程序员宅基地
技术标签: 机器视觉 diffusers 计算机视觉 stable diffusion 深度学习 人工智能 pytorch AIGC
1.简介
上一篇文章中我们介绍了SD以及scheduler,深入了解了diffusers中代码和论文公式中的相对关系。现在我们就要开始实战,看看怎么去训练和推理自己的模型。
2.pipeline
首先我们从需求出发,先要搞清楚自己的目标是什么,数据格式是什么,输入输出是什么。这里就少不了对pipeline的理解和介绍,整理下常用的几个pipeline以及Inference和Train时的相关理解(inference和train的所有相关的代码都可以在diffusers库的源码中找到):
| Pipeline | Inference | Train |
| StableDiffusionPipeline | *随机latent, *text作为内容引导, *生成image |
*data pair:image,text *image根据t加噪输入网络 |
| StableDiffusionImg2ImgPipeline | *image作为初始latent, *text作为内容引导, *生成image |
*data pair:image,text *image根据t加噪输入网络 |
| StableDiffusionDepth2ImgPipeline | *随机latent, *depth作为结构引导与latent拼接, *text作为内容引导, 生成image |
*data pair:image,depth image, text *image根据t加噪,与depth拼接后输入网络 |
| StableDiffusionInpaintPipeline | *image作为初始latent, *mask作为结构引导与latent 和maskedimage拼接, *text作为内容引导, 生成image |
*data pair:image,mask, text *image根据t加噪,与mask和masked image拼接后输入网络 |
从上方表格我分析得到以下几点:
1. text均是控制生成图像的内容,因为其是通过cross attention输入进unet中与图像产生关联。
2. depth/mask等控制生成图像的结构,均是与latent拼接后再输入进unet。
3. StableDiffusionPipeline和StableDiffusionImg2ImgPipeline的训练流程其实是一样一样的,因为输入的image如果是作为latent,那么只能作为初始的latent(diffusion原理决定,unet预测的是噪声),所以Img2Img只能让生成的image和输入的image类似,但不能稳定控制其结构。
理解了上方这几点,我们后续就很好对pipeline进行修改和自定义了。
3.实验数据
我们用fill50k数据集fusing/fill50k · Datasets at Hugging Face来作为实验数据,可以看到每条数据有一个上色的图像,一个轮廓图像,以及与上色图像对应的text,一共有50000条类似的数据。

接下来我们看看怎么来根据不同的需求来训练和推理模型。
4.Uncondition Text-to-Image
uncondition就意味着我们的输入就是text和对应的color image,推理的时候输入prompt后就会得到对应颜色的圈,但圈的位置和原始数据中的不一定对应!
因为这个就是纯粹的text-to-image,我们直接使用diffusers库中的example/text_to_image中的train_text_to_image.py就行,更改一下数据集就好:
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 accelerate launch --mixed_precision="fp16" train_text_to_image.py \
--pretrained_model_name_or_path=runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5 \
--dataset_name=fusing/fill50k \
--resolution=512 --center_crop --random_flip \
--train_batch_size=4\
--gradient_accumulation_steps=4 \
--gradient_checkpointing \
--max_train_steps=15000 \
--learning_rate=1e-05 \
--max_grad_norm=1 \
--lr_scheduler="constant" --lr_warmup_steps=0 \
--output_dir="sd-fillUncondT2I-model"若CUDA显存不足,可以调小batch_size或者使用--use_8bit_adam(至少也要16GB显存)。
训练好后我们直接StableDiffusionPipeline输入prompt推理即可,但是为了便于后续的自定义操作,我们将pipeline进行拆解,最后得到的结果和使用pipeline的结果一致(这个其实是阉割版):
import torch
from diffusers import StableDiffusionImg2ImgPipeline, UNet2DConditionModel, StableDiffusionPipeline, StableDiffusionInpaintPipeline
from PIL import Image
from torchvision import transforms
from tqdm.auto import tqdm
# 加载训练好的模型
torch_device = 'cuda:0'
model_path = "sd-fillUncondT2I-model"
unet = UNet2DConditionModel.from_pretrained(model_path + "/checkpoint-15000/unet", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5", unet=unet, torch_dtype=torch.float16)
pipe.to(torch_device)
# 参数
prompt = ["pale golden rod circle with old lace background"]
height = 512
width = 512
num_inference_steps = 50
guidance_scale = 7.5
generator = torch.manual_seed(0)
batch_size = len(prompt)
# embedding text classifier-free
text_input = pipe.tokenizer(prompt, padding="max_length", max_length=pipe.tokenizer.model_max_length, truncation=True, return_tensors="pt")
text_embeddings = pipe.text_encoder(text_input.input_ids.to(torch_device))[0]
uncond_input = pipe.tokenizer(
[""] * batch_size, padding="max_length", max_length=pipe.tokenizer.model_max_length, return_tensors="pt"
)
uncond_embeddings = pipe.text_encoder(uncond_input.input_ids.to(torch_device))[0]
text_embeddings = torch.cat([uncond_embeddings, text_embeddings])
# 初始化latent
latents = torch.randn(
(batch_size, unet.config.in_channels, height // 8, width // 8),
generator=generator,
)
latents = latents.to(torch_device).half()
# 设置scheduler
pipe.scheduler.set_timesteps(num_inference_steps)
latents = latents * pipe.scheduler.init_noise_sigma
# 去噪迭代
for t in tqdm(pipe.scheduler.timesteps):
latent_model_input = torch.cat([latents] * 2)
latent_model_input = pipe.scheduler.scale_model_input(latent_model_input, timestep=t)
with torch.no_grad():
noise_pred = unet(latent_model_input, t, encoder_hidden_states=text_embeddings).sample
noise_pred_uncond, noise_pred_text = noise_pred.chunk(2)
noise_pred = noise_pred_uncond + guidance_scale * (noise_pred_text - noise_pred_uncond)
# 计算x_t-1
latents = pipe.scheduler.step(noise_pred, t, latents).prev_sample
latents = 1 / 0.18215 * latents
with torch.no_grad():
image = pipe.vae.decode(latents).sample
# 保存image
image = (image / 2 + 0.5).clamp(0, 1)
image = image.detach().cpu().permute(0, 2, 3, 1).numpy()
images = (image * 255).round().astype("uint8")
pil_images = [Image.fromarray(image) for image in images]
pil_images[0].save("fill.png")
这里我们选取0.png对应的prompt:"pale golden rod circle with old lace background"输入网络:
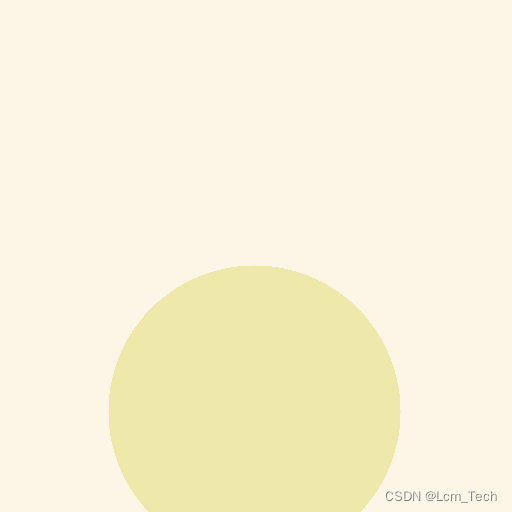

从结果中可以看到确实生成了与prompt内容相近的图像(颜色还算符合吧。。。),但生成圆圈的位置与0.png并不一致,这是因为没有加condition约束。
5.Image-Condition Text-to-Image
如果要想要根据我们给的圆圈的轮廓来生成图像,就需要将轮廓图像作为condition来输入进网络中,聪明的你肯定想到了StableDiffusionDepth2ImgPipeline和StableDiffusionInpaintPipeline,但是Depth2Img的训练script并没有给出,而Inpaint的训练script过于冗杂(需要处理mask和masked image),所以为了更好地说明流程和让大家理解,我们在train_text_to_image.py这个script上进行修改。(当然也可以用controlnet,不过这种高级且复杂的结构我们后面再讲)
我们主要在以下几个地方进行修改:
1. 加载数据集中的condition图像(轮廓图像),修改DATASET_NAME_MAPPING 使得dataset的get_item可以得到conditioning_image
DATASET_NAME_MAPPING = {
"fusing/fill50k": ("image", "conditioning_image", "text"),
}
2. 更改unet的输入通道数,以前只是latent的4通道,现在要拼接轮廓图像,所以输入通道为5
unet = UNet2DConditionModel.from_pretrained(
args.pretrained_model_name_or_path, subfolder="unet",
revision=args.non_ema_revision
)
unet.conv_in = nn.Conv2d(5, 320, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
3. condition图像的数据处理,以前只加载了color image,现在需要加载condition image并预处理,这里直接用单通道resize为对应latent大小,类似与inpaint的mask处理
# Preprocessing the datasets.
train_transforms = transforms.Compose(
[
transforms.Resize(args.resolution, interpolation=transforms.InterpolationMode.BILINEAR),
transforms.CenterCrop(args.resolution) if args.center_crop else transforms.RandomCrop(args.resolution),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize([0.5], [0.5]),
]
)
cond_transforms = transforms.Compose(
[
transforms.Resize(args.resolution // 8, interpolation=transforms.InterpolationMode.BILINEAR),
transforms.ToTensor(),
]
)
def preprocess_train(examples):
images = [image.convert("RGB") for image in examples[image_column]]
conditioning_images = [image.convert("L") for image in examples["conditioning_image"]]
examples["pixel_values"] = [train_transforms(image) for image in images]
examples["conditioning_pixel_values"] = [cond_transforms(image) for image in conditioning_images]
examples["input_ids"] = tokenize_captions(examples)
return examples4. 训练时的数据拼接,将加载后的latent与condition latent进行拼接输入unet网络
latents = vae.encode(batch["pixel_values"].to(weight_dtype)).latent_dist.sample()
latents = latents * vae.config.scaling_factor
conditioning_latents = batch["conditioning_pixel_values"].to(weight_dtype)
noisy_latents = torch.cat((noisy_latents, conditioning_latents), dim=1)
完成的代码如下:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# coding=utf-8
# Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Inc. team. All rights reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
import argparse
import logging
import math
import os
import random
import shutil
from pathlib import Path
import accelerate
import datasets
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.utils.checkpoint
import transformers
from accelerate import Accelerator
from accelerate.logging import get_logger
from accelerate.state import AcceleratorState
from accelerate.utils import ProjectConfiguration, set_seed
from datasets import load_dataset
from huggingface_hub import create_repo, upload_folder
from packaging import version
from torchvision import transforms
from tqdm.auto import tqdm
from transformers import CLIPTextModel, CLIPTokenizer
from transformers.utils import ContextManagers
import diffusers
from diffusers import AutoencoderKL, DDPMScheduler, StableDiffusionPipeline, UNet2DConditionModel
from diffusers.optimization import get_scheduler
from diffusers.training_utils import EMAModel, compute_snr
from diffusers.utils import check_min_version, deprecate, is_wandb_available, make_image_grid
from diffusers.utils.import_utils import is_xformers_available
if is_wandb_available():
import wandb
# Will error if the minimal version of diffusers is not installed. Remove at your own risks.
check_min_version("0.25.0")
logger = get_logger(__name__, log_level="INFO")
DATASET_NAME_MAPPING = {
"fusing/fill50k": ("image", "conditioning_image", "text"),
}
def save_model_card(
args,
repo_id: str,
images=None,
repo_folder=None,
):
img_str = ""
if len(images) > 0:
image_grid = make_image_grid(images, 1, len(args.validation_prompts))
image_grid.save(os.path.join(repo_folder, "val_imgs_grid.png"))
img_str += "\n"
yaml = f"""
---
license: creativeml-openrail-m
base_model: {args.pretrained_model_name_or_path}
datasets:
- {args.dataset_name}
tags:
- stable-diffusion
- stable-diffusion-diffusers
- text-to-image
- diffusers
inference: true
---
"""
model_card = f"""
# Text-to-image finetuning - {repo_id}
This pipeline was finetuned from **{args.pretrained_model_name_or_path}** on the **{args.dataset_name}** dataset. Below are some example images generated with the finetuned pipeline using the following prompts: {args.validation_prompts}: \n
{img_str}
## Pipeline usage
You can use the pipeline like so:
```python
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
import torch
pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("{repo_id}", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
prompt = "{args.validation_prompts[0]}"
image = pipeline(prompt).images[0]
image.save("my_image.png")
```
## Training info
These are the key hyperparameters used during training:
* Epochs: {args.num_train_epochs}
* Learning rate: {args.learning_rate}
* Batch size: {args.train_batch_size}
* Gradient accumulation steps: {args.gradient_accumulation_steps}
* Image resolution: {args.resolution}
* Mixed-precision: {args.mixed_precision}
"""
wandb_info = ""
if is_wandb_available():
wandb_run_url = None
if wandb.run is not None:
wandb_run_url = wandb.run.url
if wandb_run_url is not None:
wandb_info = f"""
More information on all the CLI arguments and the environment are available on your [`wandb` run page]({wandb_run_url}).
"""
model_card += wandb_info
with open(os.path.join(repo_folder, "README.md"), "w") as f:
f.write(yaml + model_card)
def log_validation(vae, text_encoder, tokenizer, unet, args, accelerator, weight_dtype, epoch):
logger.info("Running validation... ")
pipeline = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
args.pretrained_model_name_or_path,
vae=accelerator.unwrap_model(vae),
text_encoder=accelerator.unwrap_model(text_encoder),
tokenizer=tokenizer,
unet=accelerator.unwrap_model(unet),
safety_checker=None,
revision=args.revision,
variant=args.variant,
torch_dtype=weight_dtype,
)
pipeline = pipeline.to(accelerator.device)
pipeline.set_progress_bar_config(disable=True)
if args.enable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention:
pipeline.enable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention()
if args.seed is None:
generator = None
else:
generator = torch.Generator(device=accelerator.device).manual_seed(args.seed)
images = []
for i in range(len(args.validation_prompts)):
with torch.autocast("cuda"):
image = pipeline(args.validation_prompts[i], num_inference_steps=20, generator=generator).images[0]
images.append(image)
for tracker in accelerator.trackers:
if tracker.name == "tensorboard":
np_images = np.stack([np.asarray(img) for img in images])
tracker.writer.add_images("validation", np_images, epoch, dataformats="NHWC")
elif tracker.name == "wandb":
tracker.log(
{
"validation": [
wandb.Image(image, caption=f"{i}: {args.validation_prompts[i]}")
for i, image in enumerate(images)
]
}
)
else:
logger.warn(f"image logging not implemented for {tracker.name}")
del pipeline
torch.cuda.empty_cache()
return images
def parse_args():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="Simple example of a training script.")
parser.add_argument(
"--input_perturbation", type=float, default=0, help="The scale of input perturbation. Recommended 0.1."
)
parser.add_argument(
"--pretrained_model_name_or_path",
type=str,
default=None,
required=True,
help="Path to pretrained model or model identifier from huggingface.co/models.",
)
parser.add_argument(
"--revision",
type=str,
default=None,
required=False,
help="Revision of pretrained model identifier from huggingface.co/models.",
)
parser.add_argument(
"--variant",
type=str,
default=None,
help="Variant of the model files of the pretrained model identifier from huggingface.co/models, 'e.g.' fp16",
)
parser.add_argument(
"--dataset_name",
type=str,
default=None,
help=(
"The name of the Dataset (from the HuggingFace hub) to train on (could be your own, possibly private,"
" dataset). It can also be a path pointing to a local copy of a dataset in your filesystem,"
" or to a folder containing files that ?? Datasets can understand."
),
)
parser.add_argument(
"--dataset_config_name",
type=str,
default=None,
help="The config of the Dataset, leave as None if there's only one config.",
)
parser.add_argument(
"--train_data_dir",
type=str,
default=None,
help=(
"A folder containing the training data. Folder contents must follow the structure described in"
" https://huggingface.co/docs/datasets/image_dataset#imagefolder. In particular, a `metadata.jsonl` file"
" must exist to provide the captions for the images. Ignored if `dataset_name` is specified."
),
)
parser.add_argument(
"--image_column", type=str, default="image", help="The column of the dataset containing an image."
)
parser.add_argument(
"--caption_column",
type=str,
default="text",
help="The column of the dataset containing a caption or a list of captions.",
)
parser.add_argument(
"--max_train_samples",
type=int,
default=None,
help=(
"For debugging purposes or quicker training, truncate the number of training examples to this "
"value if set."
),
)
parser.add_argument(
"--validation_prompts",
type=str,
default=None,
nargs="+",
help=("A set of prompts evaluated every `--validation_epochs` and logged to `--report_to`."),
)
parser.add_argument(
"--output_dir",
type=str,
default="sd-model-finetuned",
help="The output directory where the model predictions and checkpoints will be written.",
)
parser.add_argument(
"--cache_dir",
type=str,
default=None,
help="The directory where the downloaded models and datasets will be stored.",
)
parser.add_argument("--seed", type=int, default=None, help="A seed for reproducible training.")
parser.add_argument(
"--resolution",
type=int,
default=512,
help=(
"The resolution for input images, all the images in the train/validation dataset will be resized to this"
" resolution"
),
)
parser.add_argument(
"--center_crop",
default=False,
action="store_true",
help=(
"Whether to center crop the input images to the resolution. If not set, the images will be randomly"
" cropped. The images will be resized to the resolution first before cropping."
),
)
parser.add_argument(
"--random_flip",
action="store_true",
help="whether to randomly flip images horizontally",
)
parser.add_argument(
"--train_batch_size", type=int, default=16, help="Batch size (per device) for the training dataloader."
)
parser.add_argument("--num_train_epochs", type=int, default=100)
parser.add_argument(
"--max_train_steps",
type=int,
default=None,
help="Total number of training steps to perform. If provided, overrides num_train_epochs.",
)
parser.add_argument(
"--gradient_accumulation_steps",
type=int,
default=1,
help="Number of updates steps to accumulate before performing a backward/update pass.",
)
parser.add_argument(
"--gradient_checkpointing",
action="store_true",
help="Whether or not to use gradient checkpointing to save memory at the expense of slower backward pass.",
)
parser.add_argument(
"--learning_rate",
type=float,
default=1e-4,
help="Initial learning rate (after the potential warmup period) to use.",
)
parser.add_argument(
"--scale_lr",
action="store_true",
default=False,
help="Scale the learning rate by the number of GPUs, gradient accumulation steps, and batch size.",
)
parser.add_argument(
"--lr_scheduler",
type=str,
default="constant",
help=(
'The scheduler type to use. Choose between ["linear", "cosine", "cosine_with_restarts", "polynomial",'
' "constant", "constant_with_warmup"]'
),
)
parser.add_argument(
"--lr_warmup_steps", type=int, default=500, help="Number of steps for the warmup in the lr scheduler."
)
parser.add_argument(
"--snr_gamma",
type=float,
default=None,
help="SNR weighting gamma to be used if rebalancing the loss. Recommended value is 5.0. "
"More details here: https://arxiv.org/abs/2303.09556.",
)
parser.add_argument(
"--use_8bit_adam", action="store_true", help="Whether or not to use 8-bit Adam from bitsandbytes."
)
parser.add_argument(
"--allow_tf32",
action="store_true",
help=(
"Whether or not to allow TF32 on Ampere GPUs. Can be used to speed up training. For more information, see"
" https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/notes/cuda.html#tensorfloat-32-tf32-on-ampere-devices"
),
)
parser.add_argument("--use_ema", action="store_true", help="Whether to use EMA model.")
parser.add_argument(
"--non_ema_revision",
type=str,
default=None,
required=False,
help=(
"Revision of pretrained non-ema model identifier. Must be a branch, tag or git identifier of the local or"
" remote repository specified with --pretrained_model_name_or_path."
),
)
parser.add_argument(
"--dataloader_num_workers",
type=int,
default=0,
help=(
"Number of subprocesses to use for data loading. 0 means that the data will be loaded in the main process."
),
)
parser.add_argument("--adam_beta1", type=float, default=0.9, help="The beta1 parameter for the Adam optimizer.")
parser.add_argument("--adam_beta2", type=float, default=0.999, help="The beta2 parameter for the Adam optimizer.")
parser.add_argument("--adam_weight_decay", type=float, default=1e-2, help="Weight decay to use.")
parser.add_argument("--adam_epsilon", type=float, default=1e-08, help="Epsilon value for the Adam optimizer")
parser.add_argument("--max_grad_norm", default=1.0, type=float, help="Max gradient norm.")
parser.add_argument("--push_to_hub", action="store_true", help="Whether or not to push the model to the Hub.")
parser.add_argument("--hub_token", type=str, default=None, help="The token to use to push to the Model Hub.")
parser.add_argument(
"--prediction_type",
type=str,
default=None,
help="The prediction_type that shall be used for training. Choose between 'epsilon' or 'v_prediction' or leave `None`. If left to `None` the default prediction type of the scheduler: `noise_scheduler.config.prediciton_type` is chosen.",
)
parser.add_argument(
"--hub_model_id",
type=str,
default=None,
help="The name of the repository to keep in sync with the local `output_dir`.",
)
parser.add_argument(
"--logging_dir",
type=str,
default="logs",
help=(
"[TensorBoard](https://www.tensorflow.org/tensorboard) log directory. Will default to"
" *output_dir/runs/**CURRENT_DATETIME_HOSTNAME***."
),
)
parser.add_argument(
"--mixed_precision",
type=str,
default=None,
choices=["no", "fp16", "bf16"],
help=(
"Whether to use mixed precision. Choose between fp16 and bf16 (bfloat16). Bf16 requires PyTorch >="
" 1.10.and an Nvidia Ampere GPU. Default to the value of accelerate config of the current system or the"
" flag passed with the `accelerate.launch` command. Use this argument to override the accelerate config."
),
)
parser.add_argument(
"--report_to",
type=str,
default="tensorboard",
help=(
'The integration to report the results and logs to. Supported platforms are `"tensorboard"`'
' (default), `"wandb"` and `"comet_ml"`. Use `"all"` to report to all integrations.'
),
)
parser.add_argument("--local_rank", type=int, default=-1, help="For distributed training: local_rank")
parser.add_argument(
"--checkpointing_steps",
type=int,
default=500,
help=(
"Save a checkpoint of the training state every X updates. These checkpoints are only suitable for resuming"
" training using `--resume_from_checkpoint`."
),
)
parser.add_argument(
"--checkpoints_total_limit",
type=int,
default=None,
help=("Max number of checkpoints to store."),
)
parser.add_argument(
"--resume_from_checkpoint",
type=str,
default=None,
help=(
"Whether training should be resumed from a previous checkpoint. Use a path saved by"
' `--checkpointing_steps`, or `"latest"` to automatically select the last available checkpoint.'
),
)
parser.add_argument(
"--enable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention", action="store_true", help="Whether or not to use xformers."
)
parser.add_argument("--noise_offset", type=float, default=0, help="The scale of noise offset.")
parser.add_argument(
"--validation_epochs",
type=int,
default=5,
help="Run validation every X epochs.",
)
parser.add_argument(
"--tracker_project_name",
type=str,
default="text2image-fine-tune",
help=(
"The `project_name` argument passed to Accelerator.init_trackers for"
" more information see https://huggingface.co/docs/accelerate/v0.17.0/en/package_reference/accelerator#accelerate.Accelerator"
),
)
args = parser.parse_args()
env_local_rank = int(os.environ.get("LOCAL_RANK", -1))
if env_local_rank != -1 and env_local_rank != args.local_rank:
args.local_rank = env_local_rank
# Sanity checks
if args.dataset_name is None and args.train_data_dir is None:
raise ValueError("Need either a dataset name or a training folder.")
# default to using the same revision for the non-ema model if not specified
if args.non_ema_revision is None:
args.non_ema_revision = args.revision
return args
def main():
args = parse_args()
if args.non_ema_revision is not None:
deprecate(
"non_ema_revision!=None",
"0.15.0",
message=(
"Downloading 'non_ema' weights from revision branches of the Hub is deprecated. Please make sure to"
" use `--variant=non_ema` instead."
),
)
logging_dir = os.path.join(args.output_dir, args.logging_dir)
accelerator_project_config = ProjectConfiguration(project_dir=args.output_dir, logging_dir=logging_dir)
accelerator = Accelerator(
gradient_accumulation_steps=args.gradient_accumulation_steps,
mixed_precision=args.mixed_precision,
log_with=args.report_to,
project_config=accelerator_project_config,
)
# Make one log on every process with the configuration for debugging.
logging.basicConfig(
format="%(asctime)s - %(levelname)s - %(name)s - %(message)s",
datefmt="%m/%d/%Y %H:%M:%S",
level=logging.INFO,
)
logger.info(accelerator.state, main_process_only=False)
if accelerator.is_local_main_process:
datasets.utils.logging.set_verbosity_warning()
transformers.utils.logging.set_verbosity_warning()
diffusers.utils.logging.set_verbosity_info()
else:
datasets.utils.logging.set_verbosity_error()
transformers.utils.logging.set_verbosity_error()
diffusers.utils.logging.set_verbosity_error()
# If passed along, set the training seed now.
if args.seed is not None:
set_seed(args.seed)
# Handle the repository creation
if accelerator.is_main_process:
if args.output_dir is not None:
os.makedirs(args.output_dir, exist_ok=True)
if args.push_to_hub:
repo_id = create_repo(
repo_id=args.hub_model_id or Path(args.output_dir).name, exist_ok=True, token=args.hub_token
).repo_id
# Load scheduler, tokenizer and models.
noise_scheduler = DDPMScheduler.from_pretrained(args.pretrained_model_name_or_path, subfolder="scheduler")
tokenizer = CLIPTokenizer.from_pretrained(
args.pretrained_model_name_or_path, subfolder="tokenizer", revision=args.revision
)
def deepspeed_zero_init_disabled_context_manager():
"""
returns either a context list that includes one that will disable zero.Init or an empty context list
"""
deepspeed_plugin = AcceleratorState().deepspeed_plugin if accelerate.state.is_initialized() else None
if deepspeed_plugin is None:
return []
return [deepspeed_plugin.zero3_init_context_manager(enable=False)]
# Currently Accelerate doesn't know how to handle multiple models under Deepspeed ZeRO stage 3.
# For this to work properly all models must be run through `accelerate.prepare`. But accelerate
# will try to assign the same optimizer with the same weights to all models during
# `deepspeed.initialize`, which of course doesn't work.
#
# For now the following workaround will partially support Deepspeed ZeRO-3, by excluding the 2
# frozen models from being partitioned during `zero.Init` which gets called during
# `from_pretrained` So CLIPTextModel and AutoencoderKL will not enjoy the parameter sharding
# across multiple gpus and only UNet2DConditionModel will get ZeRO sharded.
with ContextManagers(deepspeed_zero_init_disabled_context_manager()):
text_encoder = CLIPTextModel.from_pretrained(
args.pretrained_model_name_or_path, subfolder="text_encoder", revision=args.revision, variant=args.variant
)
vae = AutoencoderKL.from_pretrained(
args.pretrained_model_name_or_path, subfolder="vae", revision=args.revision, variant=args.variant
)
unet = UNet2DConditionModel.from_pretrained(
args.pretrained_model_name_or_path, subfolder="unet", revision=args.non_ema_revision
)
# print(unet)
unet.conv_in = nn.Conv2d(5, 320, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
# Freeze vae and text_encoder and set unet to trainable
vae.requires_grad_(False)
text_encoder.requires_grad_(False)
unet.train()
# Create EMA for the unet.
if args.use_ema:
ema_unet = UNet2DConditionModel.from_pretrained(
args.pretrained_model_name_or_path, subfolder="unet", revision=args.revision, variant=args.variant
)
ema_unet.conv_in = nn.Conv2d(5, 320, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
ema_unet = EMAModel(ema_unet.parameters(), model_cls=UNet2DConditionModel, model_config=ema_unet.config)
if args.enable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention:
if is_xformers_available():
import xformers
xformers_version = version.parse(xformers.__version__)
if xformers_version == version.parse("0.0.16"):
logger.warn(
"xFormers 0.0.16 cannot be used for training in some GPUs. If you observe problems during training, please update xFormers to at least 0.0.17. See https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/optimization/xformers for more details."
)
unet.enable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention()
else:
raise ValueError("xformers is not available. Make sure it is installed correctly")
# `accelerate` 0.16.0 will have better support for customized saving
if version.parse(accelerate.__version__) >= version.parse("0.16.0"):
# create custom saving & loading hooks so that `accelerator.save_state(...)` serializes in a nice format
def save_model_hook(models, weights, output_dir):
if accelerator.is_main_process:
if args.use_ema:
ema_unet.save_pretrained(os.path.join(output_dir, "unet_ema"))
for i, model in enumerate(models):
model.save_pretrained(os.path.join(output_dir, "unet"))
# make sure to pop weight so that corresponding model is not saved again
weights.pop()
def load_model_hook(models, input_dir):
if args.use_ema:
load_model = EMAModel.from_pretrained(os.path.join(input_dir, "unet_ema"), UNet2DConditionModel)
ema_unet.load_state_dict(load_model.state_dict())
ema_unet.to(accelerator.device)
del load_model
for i in range(len(models)):
# pop models so that they are not loaded again
model = models.pop()
# load diffusers style into model
load_model = UNet2DConditionModel.from_pretrained(input_dir, subfolder="unet")
model.register_to_config(**load_model.config)
model.load_state_dict(load_model.state_dict())
del load_model
accelerator.register_save_state_pre_hook(save_model_hook)
accelerator.register_load_state_pre_hook(load_model_hook)
if args.gradient_checkpointing:
unet.enable_gradient_checkpointing()
# Enable TF32 for faster training on Ampere GPUs,
# cf https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/notes/cuda.html#tensorfloat-32-tf32-on-ampere-devices
if args.allow_tf32:
torch.backends.cuda.matmul.allow_tf32 = True
if args.scale_lr:
args.learning_rate = (
args.learning_rate * args.gradient_accumulation_steps * args.train_batch_size * accelerator.num_processes
)
# Initialize the optimizer
if args.use_8bit_adam:
try:
import bitsandbytes as bnb
except ImportError:
raise ImportError(
"Please install bitsandbytes to use 8-bit Adam. You can do so by running `pip install bitsandbytes`"
)
optimizer_cls = bnb.optim.AdamW8bit
else:
optimizer_cls = torch.optim.AdamW
optimizer = optimizer_cls(
unet.parameters(),
lr=args.learning_rate,
betas=(args.adam_beta1, args.adam_beta2),
weight_decay=args.adam_weight_decay,
eps=args.adam_epsilon,
)
# Get the datasets: you can either provide your own training and evaluation files (see below)
# or specify a Dataset from the hub (the dataset will be downloaded automatically from the datasets Hub).
# In distributed training, the load_dataset function guarantees that only one local process can concurrently
# download the dataset.
if args.dataset_name is not None:
# Downloading and loading a dataset from the hub.
dataset = load_dataset(
args.dataset_name,
args.dataset_config_name,
cache_dir=args.cache_dir,
data_dir=args.train_data_dir,
)
else:
data_files = {}
if args.train_data_dir is not None:
data_files["train"] = os.path.join(args.train_data_dir, "**")
dataset = load_dataset(
"imagefolder",
data_files=data_files,
cache_dir=args.cache_dir,
)
# See more about loading custom images at
# https://huggingface.co/docs/datasets/v2.4.0/en/image_load#imagefolder
# Preprocessing the datasets.
# We need to tokenize inputs and targets.
column_names = dataset["train"].column_names
# 6. Get the column names for input/target.
dataset_columns = DATASET_NAME_MAPPING.get(args.dataset_name, None)
if args.image_column is None:
image_column = dataset_columns[0] if dataset_columns is not None else column_names[0]
else:
image_column = args.image_column
if image_column not in column_names:
raise ValueError(
f"--image_column' value '{args.image_column}' needs to be one of: {', '.join(column_names)}"
)
if args.caption_column is None:
caption_column = dataset_columns[1] if dataset_columns is not None else column_names[1]
else:
caption_column = args.caption_column
if caption_column not in column_names:
raise ValueError(
f"--caption_column' value '{args.caption_column}' needs to be one of: {', '.join(column_names)}"
)
# Preprocessing the datasets.
# We need to tokenize input captions and transform the images.
def tokenize_captions(examples, is_train=True):
captions = []
for caption in examples[caption_column]:
if isinstance(caption, str):
captions.append(caption)
elif isinstance(caption, (list, np.ndarray)):
# take a random caption if there are multiple
captions.append(random.choice(caption) if is_train else caption[0])
else:
raise ValueError(
f"Caption column `{caption_column}` should contain either strings or lists of strings."
)
inputs = tokenizer(
captions, max_length=tokenizer.model_max_length, padding="max_length", truncation=True, return_tensors="pt"
)
return inputs.input_ids
# Preprocessing the datasets.
train_transforms = transforms.Compose(
[
transforms.Resize(args.resolution, interpolation=transforms.InterpolationMode.BILINEAR),
transforms.CenterCrop(args.resolution) if args.center_crop else transforms.RandomCrop(args.resolution),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize([0.5], [0.5]),
]
)
cond_transforms = transforms.Compose(
[
transforms.Resize(args.resolution // 8, interpolation=transforms.InterpolationMode.BILINEAR),
transforms.ToTensor(),
]
)
def preprocess_train(examples):
images = [image.convert("RGB") for image in examples[image_column]]
conditioning_images = [image.convert("L") for image in examples["conditioning_image"]]
examples["pixel_values"] = [train_transforms(image) for image in images]
examples["conditioning_pixel_values"] = [cond_transforms(image) for image in conditioning_images]
examples["input_ids"] = tokenize_captions(examples)
return examples
with accelerator.main_process_first():
if args.max_train_samples is not None:
dataset["train"] = dataset["train"].shuffle(seed=args.seed).select(range(args.max_train_samples))
# Set the training transforms
train_dataset = dataset["train"].with_transform(preprocess_train)
def collate_fn(examples):
pixel_values = torch.stack([example["pixel_values"] for example in examples])
pixel_values = pixel_values.to(memory_format=torch.contiguous_format).float()
conditioning_pixel_values = torch.stack([example["conditioning_pixel_values"] for example in examples])
conditioning_pixel_values = conditioning_pixel_values.to(memory_format=torch.contiguous_format).float()
input_ids = torch.stack([example["input_ids"] for example in examples])
return {"pixel_values": pixel_values, "input_ids": input_ids, "conditioning_pixel_values": conditioning_pixel_values}
# DataLoaders creation:
train_dataloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
train_dataset,
shuffle=True,
collate_fn=collate_fn,
batch_size=args.train_batch_size,
num_workers=args.dataloader_num_workers,
)
# Scheduler and math around the number of training steps.
overrode_max_train_steps = False
num_update_steps_per_epoch = math.ceil(len(train_dataloader) / args.gradient_accumulation_steps)
if args.max_train_steps is None:
args.max_train_steps = args.num_train_epochs * num_update_steps_per_epoch
overrode_max_train_steps = True
lr_scheduler = get_scheduler(
args.lr_scheduler,
optimizer=optimizer,
num_warmup_steps=args.lr_warmup_steps * accelerator.num_processes,
num_training_steps=args.max_train_steps * accelerator.num_processes,
)
# Prepare everything with our `accelerator`.
unet, optimizer, train_dataloader, lr_scheduler = accelerator.prepare(
unet, optimizer, train_dataloader, lr_scheduler
)
if args.use_ema:
ema_unet.to(accelerator.device)
# For mixed precision training we cast all non-trainable weigths (vae, non-lora text_encoder and non-lora unet) to half-precision
# as these weights are only used for inference, keeping weights in full precision is not required.
weight_dtype = torch.float32
if accelerator.mixed_precision == "fp16":
weight_dtype = torch.float16
args.mixed_precision = accelerator.mixed_precision
elif accelerator.mixed_precision == "bf16":
weight_dtype = torch.bfloat16
args.mixed_precision = accelerator.mixed_precision
# Move text_encode and vae to gpu and cast to weight_dtype
text_encoder.to(accelerator.device, dtype=weight_dtype)
vae.to(accelerator.device, dtype=weight_dtype)
# We need to recalculate our total training steps as the size of the training dataloader may have changed.
num_update_steps_per_epoch = math.ceil(len(train_dataloader) / args.gradient_accumulation_steps)
if overrode_max_train_steps:
args.max_train_steps = args.num_train_epochs * num_update_steps_per_epoch
# Afterwards we recalculate our number of training epochs
args.num_train_epochs = math.ceil(args.max_train_steps / num_update_steps_per_epoch)
# We need to initialize the trackers we use, and also store our configuration.
# The trackers initializes automatically on the main process.
if accelerator.is_main_process:
tracker_config = dict(vars(args))
tracker_config.pop("validation_prompts")
accelerator.init_trackers(args.tracker_project_name, tracker_config)
# Train!
total_batch_size = args.train_batch_size * accelerator.num_processes * args.gradient_accumulation_steps
logger.info("***** Running training *****")
logger.info(f" Num examples = {len(train_dataset)}")
logger.info(f" Num Epochs = {args.num_train_epochs}")
logger.info(f" Instantaneous batch size per device = {args.train_batch_size}")
logger.info(f" Total train batch size (w. parallel, distributed & accumulation) = {total_batch_size}")
logger.info(f" Gradient Accumulation steps = {args.gradient_accumulation_steps}")
logger.info(f" Total optimization steps = {args.max_train_steps}")
global_step = 0
first_epoch = 0
# Potentially load in the weights and states from a previous save
if args.resume_from_checkpoint:
if args.resume_from_checkpoint != "latest":
path = os.path.basename(args.resume_from_checkpoint)
else:
# Get the most recent checkpoint
dirs = os.listdir(args.output_dir)
dirs = [d for d in dirs if d.startswith("checkpoint")]
dirs = sorted(dirs, key=lambda x: int(x.split("-")[1]))
path = dirs[-1] if len(dirs) > 0 else None
if path is None:
accelerator.print(
f"Checkpoint '{args.resume_from_checkpoint}' does not exist. Starting a new training run."
)
args.resume_from_checkpoint = None
initial_global_step = 0
else:
accelerator.print(f"Resuming from checkpoint {path}")
accelerator.load_state(os.path.join(args.output_dir, path))
global_step = int(path.split("-")[1])
initial_global_step = global_step
first_epoch = global_step // num_update_steps_per_epoch
else:
initial_global_step = 0
progress_bar = tqdm(
range(0, args.max_train_steps),
initial=initial_global_step,
desc="Steps",
# Only show the progress bar once on each machine.
disable=not accelerator.is_local_main_process,
)
for epoch in range(first_epoch, args.num_train_epochs):
train_loss = 0.0
for step, batch in enumerate(train_dataloader):
with accelerator.accumulate(unet):
# Convert images to latent space
latents = vae.encode(batch["pixel_values"].to(weight_dtype)).latent_dist.sample()
latents = latents * vae.config.scaling_factor
conditioning_latents = batch["conditioning_pixel_values"].to(weight_dtype)
# Sample noise that we'll add to the latents
noise = torch.randn_like(latents)
if args.noise_offset:
# https://www.crosslabs.org//blog/diffusion-with-offset-noise
noise += args.noise_offset * torch.randn(
(latents.shape[0], latents.shape[1], 1, 1), device=latents.device
)
if args.input_perturbation:
new_noise = noise + args.input_perturbation * torch.randn_like(noise)
bsz = latents.shape[0]
# Sample a random timestep for each image
timesteps = torch.randint(0, noise_scheduler.config.num_train_timesteps, (bsz,), device=latents.device)
timesteps = timesteps.long()
# Add noise to the latents according to the noise magnitude at each timestep
# (this is the forward diffusion process)
if args.input_perturbation:
noisy_latents = noise_scheduler.add_noise(latents, new_noise, timesteps)
else:
noisy_latents = noise_scheduler.add_noise(latents, noise, timesteps)
noisy_latents = torch.cat((noisy_latents, conditioning_latents), dim=1)
# Get the text embedding for conditioning
encoder_hidden_states = text_encoder(batch["input_ids"])[0]
# Get the target for loss depending on the prediction type
if args.prediction_type is not None:
# set prediction_type of scheduler if defined
noise_scheduler.register_to_config(prediction_type=args.prediction_type)
if noise_scheduler.config.prediction_type == "epsilon":
target = noise
elif noise_scheduler.config.prediction_type == "v_prediction":
target = noise_scheduler.get_velocity(latents, noise, timesteps)
else:
raise ValueError(f"Unknown prediction type {noise_scheduler.config.prediction_type}")
# Predict the noise residual and compute loss
model_pred = unet(noisy_latents, timesteps, encoder_hidden_states).sample
if args.snr_gamma is None:
loss = F.mse_loss(model_pred.float(), target.float(), reduction="mean")
else:
# Compute loss-weights as per Section 3.4 of https://arxiv.org/abs/2303.09556.
# Since we predict the noise instead of x_0, the original formulation is slightly changed.
# This is discussed in Section 4.2 of the same paper.
snr = compute_snr(noise_scheduler, timesteps)
if noise_scheduler.config.prediction_type == "v_prediction":
# Velocity objective requires that we add one to SNR values before we divide by them.
snr = snr + 1
mse_loss_weights = (
torch.stack([snr, args.snr_gamma * torch.ones_like(timesteps)], dim=1).min(dim=1)[0] / snr
)
loss = F.mse_loss(model_pred.float(), target.float(), reduction="none")
loss = loss.mean(dim=list(range(1, len(loss.shape)))) * mse_loss_weights
loss = loss.mean()
# Gather the losses across all processes for logging (if we use distributed training).
avg_loss = accelerator.gather(loss.repeat(args.train_batch_size)).mean()
train_loss += avg_loss.item() / args.gradient_accumulation_steps
# Backpropagate
accelerator.backward(loss)
if accelerator.sync_gradients:
accelerator.clip_grad_norm_(unet.parameters(), args.max_grad_norm)
optimizer.step()
lr_scheduler.step()
optimizer.zero_grad()
# Checks if the accelerator has performed an optimization step behind the scenes
if accelerator.sync_gradients:
if args.use_ema:
ema_unet.step(unet.parameters())
progress_bar.update(1)
global_step += 1
accelerator.log({"train_loss": train_loss}, step=global_step)
train_loss = 0.0
if global_step % args.checkpointing_steps == 0:
if accelerator.is_main_process:
# _before_ saving state, check if this save would set us over the `checkpoints_total_limit`
if args.checkpoints_total_limit is not None:
checkpoints = os.listdir(args.output_dir)
checkpoints = [d for d in checkpoints if d.startswith("checkpoint")]
checkpoints = sorted(checkpoints, key=lambda x: int(x.split("-")[1]))
# before we save the new checkpoint, we need to have at _most_ `checkpoints_total_limit - 1` checkpoints
if len(checkpoints) >= args.checkpoints_total_limit:
num_to_remove = len(checkpoints) - args.checkpoints_total_limit + 1
removing_checkpoints = checkpoints[0:num_to_remove]
logger.info(
f"{len(checkpoints)} checkpoints already exist, removing {len(removing_checkpoints)} checkpoints"
)
logger.info(f"removing checkpoints: {', '.join(removing_checkpoints)}")
for removing_checkpoint in removing_checkpoints:
removing_checkpoint = os.path.join(args.output_dir, removing_checkpoint)
shutil.rmtree(removing_checkpoint)
save_path = os.path.join(args.output_dir, f"checkpoint-{global_step}")
accelerator.save_state(save_path)
logger.info(f"Saved state to {save_path}")
logs = {"step_loss": loss.detach().item(), "lr": lr_scheduler.get_last_lr()[0]}
progress_bar.set_postfix(**logs)
if global_step >= args.max_train_steps:
break
if accelerator.is_main_process:
if args.validation_prompts is not None and epoch % args.validation_epochs == 0:
if args.use_ema:
# Store the UNet parameters temporarily and load the EMA parameters to perform inference.
ema_unet.store(unet.parameters())
ema_unet.copy_to(unet.parameters())
log_validation(
vae,
text_encoder,
tokenizer,
unet,
args,
accelerator,
weight_dtype,
global_step,
)
if args.use_ema:
# Switch back to the original UNet parameters.
ema_unet.restore(unet.parameters())
# Create the pipeline using the trained modules and save it.
accelerator.wait_for_everyone()
if accelerator.is_main_process:
unet = accelerator.unwrap_model(unet)
if args.use_ema:
ema_unet.copy_to(unet.parameters())
pipeline = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
args.pretrained_model_name_or_path,
text_encoder=text_encoder,
vae=vae,
unet=unet,
revision=args.revision,
variant=args.variant,
)
pipeline.save_pretrained(args.output_dir)
# Run a final round of inference.
images = []
if args.validation_prompts is not None:
logger.info("Running inference for collecting generated images...")
pipeline = pipeline.to(accelerator.device)
pipeline.torch_dtype = weight_dtype
pipeline.set_progress_bar_config(disable=True)
if args.enable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention:
pipeline.enable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention()
if args.seed is None:
generator = None
else:
generator = torch.Generator(device=accelerator.device).manual_seed(args.seed)
for i in range(len(args.validation_prompts)):
with torch.autocast("cuda"):
image = pipeline(args.validation_prompts[i], num_inference_steps=20, generator=generator).images[0]
images.append(image)
if args.push_to_hub:
save_model_card(args, repo_id, images, repo_folder=args.output_dir)
upload_folder(
repo_id=repo_id,
folder_path=args.output_dir,
commit_message="End of training",
ignore_patterns=["step_*", "epoch_*"],
)
accelerator.end_training()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()上面的训练script和之前的运行方式一样,推理代码也需要对应修改,主要修改地方有3点:
1. 加载condition图像并预处理,这里我们想要生成图像与哪个轮廓图像对应,就加载哪个轮廓图像作为约束,这里使用的是1.png
# 加载condition图像并预处理
conditioning_images = Image.open('fill50k/conditioning_images/1.png').convert('L')
cond_transforms = transforms.Compose(
[
transforms.Resize(512 // 8, interpolation=transforms.InterpolationMode.BILINEAR),
transforms.ToTensor(),
]
)
conditioning_latents = cond_transforms(conditioning_images).to(torch_device).half().unsqueeze(0)2. 反向扩散时将condition latents与latents拼接输入网络,这里是对应训练时的操作
latent_model_input = torch.cat([latents] * 2)
latent_model_input = pipe.scheduler.scale_model_input(latent_model_input, timestep=t)
latent_model_input = torch.cat((latent_model_input, conditioning_latents), dim=1)
with torch.no_grad():
noise_pred = unet(latent_model_input, t, encoder_hidden_states=text_embeddings).sample3. 修改对应unet checkpoint中unet/config.json中的in_channels=5,因为我们训练时保存的weights是5通道输入的,但是保存时并没有设置config.json中的参数,所以这里是为了初始化模型和加载checkpoint时对应
完整inference代码如下:
import torch
from diffusers import StableDiffusionImg2ImgPipeline, UNet2DConditionModel, StableDiffusionPipeline, StableDiffusionInpaintPipeline
from PIL import Image
from torchvision import transforms
import torch.nn as nn
from tqdm.auto import tqdm
# 加载模型
torch_device = 'cuda:0'
model_path = "sd-fillImgcondT2I-model"
unet = UNet2DConditionModel.from_pretrained(model_path + "/checkpoint-15000/unet", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5", unet=unet, torch_dtype=torch.float16)
pipe.to(torch_device)
# 加载condition图像并预处理
conditioning_images = Image.open('fill50k/conditioning_images/1.png').convert('L')
cond_transforms = transforms.Compose(
[
transforms.Resize(512 // 8, interpolation=transforms.InterpolationMode.BILINEAR),
transforms.ToTensor(),
]
)
conditioning_latents = cond_transforms(conditioning_images).to(torch_device).half().unsqueeze(0)
prompt = ["pale golden rod circle with old lace background"]
# 参数
height = 512
width = 512
num_inference_steps = 50
guidance_scale = 7.5
generator = torch.manual_seed(42)
batch_size = len(prompt)
# embed text
text_input = pipe.tokenizer(prompt, padding="max_length", max_length=pipe.tokenizer.model_max_length, truncation=True, return_tensors="pt")
text_embeddings = pipe.text_encoder(text_input.input_ids.to(torch_device))[0]
uncond_input = pipe.tokenizer(
[""] * batch_size, padding="max_length", max_length=pipe.tokenizer.model_max_length, return_tensors="pt"
)
uncond_embeddings = pipe.text_encoder(uncond_input.input_ids.to(torch_device))[0]
text_embeddings = torch.cat([uncond_embeddings, text_embeddings])
# 初始化latent
latents = torch.randn(
(batch_size, 4, height // 8, width // 8),
generator=generator,
)
latents = latents.to(torch_device).half()
# 设置scheduler
pipe.scheduler.set_timesteps(num_inference_steps)
latents = latents * pipe.scheduler.init_noise_sigma
# cat condition image使shape与latent对应
conditioning_latents = torch.cat([conditioning_latents] * 2)
# 反向扩散迭代
for t in tqdm(pipe.scheduler.timesteps):
latent_model_input = torch.cat([latents] * 2)
latent_model_input = pipe.scheduler.scale_model_input(latent_model_input, timestep=t)
latent_model_input = torch.cat((latent_model_input, conditioning_latents), dim=1)
with torch.no_grad():
noise_pred = unet(latent_model_input, t, encoder_hidden_states=text_embeddings).sample
noise_pred_uncond, noise_pred_text = noise_pred.chunk(2)
noise_pred = noise_pred_uncond + guidance_scale * (noise_pred_text - noise_pred_uncond)
latents = pipe.scheduler.step(noise_pred, t, latents).prev_sample
latents = 1 / 0.18215 * latents
with torch.no_grad():
image = pipe.vae.decode(latents).sample
# 保存图像
image = (image / 2 + 0.5).clamp(0, 1)
image = image.detach().cpu().permute(0, 2, 3, 1).numpy()
images = (image * 255).round().astype("uint8")
pil_images = [Image.fromarray(image) for image in images]
pil_images[0].save("fill.png")
这里我们选取相同prompt,然后用1.png的轮廓图像输入网络:
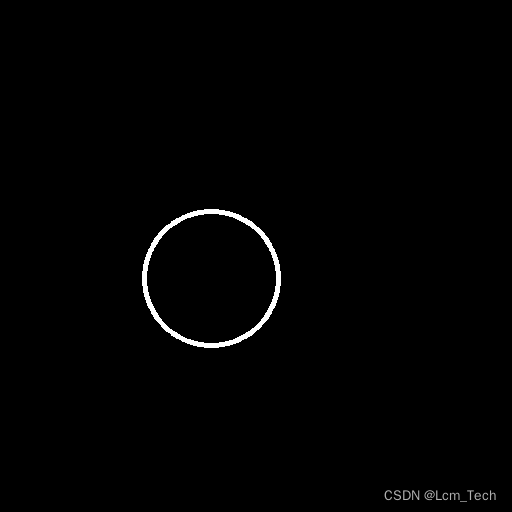


从结果中可以看到确实生成了与prompt内容对应的图像,且位置与轮廓图像中对应。至此我们就通过自定义,完成了对生成图像结构上的约束。
完整代码可以在我的github中找到,喜欢的话麻烦点个小星星哦~
下一篇文章里我们会继续深入SD的自定义,寻找使用不同格式的condition来约束生成图像的结构和内容的方法。
业务合作/学习交流+v:lizhiTechnology
如果想要了解更多diffusers相关知识,可以参考我的专栏和其他相关文章:
【diffusers】(一) diffusers库介绍 & 框架代码解析-程序员宅基地
【diffusers】(二) scheduler介绍 & 代码解析_ddpmscheduler-程序员宅基地
【diffusers】(三) pipeline原理及自定义训练推理-程序员宅基地
如果想要了解更多深度学习相关知识,可以参考我的其他文章:
【优化器】(一) SGD原理 & pytorch代码解析_sgd优化器-程序员宅基地
智能推荐
c# 调用c++ lib静态库_c#调用lib-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读2w次,点赞7次,收藏51次。四个步骤1.创建C++ Win32项目动态库dll 2.在Win32项目动态库中添加 外部依赖项 lib头文件和lib库3.导出C接口4.c#调用c++动态库开始你的表演...①创建一个空白的解决方案,在解决方案中添加 Visual C++ , Win32 项目空白解决方案的创建:添加Visual C++ , Win32 项目这......_c#调用lib
deepin/ubuntu安装苹方字体-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读4.6k次。苹方字体是苹果系统上的黑体,挺好看的。注重颜值的网站都会使用,例如知乎:font-family: -apple-system, BlinkMacSystemFont, Helvetica Neue, PingFang SC, Microsoft YaHei, Source Han Sans SC, Noto Sans CJK SC, W..._ubuntu pingfang
html表单常见操作汇总_html表单的处理程序有那些-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读159次。表单表单概述表单标签表单域按钮控件demo表单标签表单标签基本语法结构<form action="处理数据程序的url地址“ method=”get|post“ name="表单名称”></form><!--action,当提交表单时,向何处发送表单中的数据,地址可以是相对地址也可以是绝对地址--><!--method将表单中的数据传送给服务器处理,get方式直接显示在url地址中,数据可以被缓存,且长度有限制;而post方式数据隐藏传输,_html表单的处理程序有那些
PHP设置谷歌验证器(Google Authenticator)实现操作二步验证_php otp 验证器-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读1.2k次。使用说明:开启Google的登陆二步验证(即Google Authenticator服务)后用户登陆时需要输入额外由手机客户端生成的一次性密码。实现Google Authenticator功能需要服务器端和客户端的支持。服务器端负责密钥的生成、验证一次性密码是否正确。客户端记录密钥后生成一次性密码。下载谷歌验证类库文件放到项目合适位置(我这边放在项目Vender下面)https://github.com/PHPGangsta/GoogleAuthenticatorPHP代码示例://引入谷_php otp 验证器
【Python】matplotlib.plot画图横坐标混乱及间隔处理_matplotlib更改横轴间距-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读4.3k次,点赞5次,收藏11次。matplotlib.plot画图横坐标混乱及间隔处理_matplotlib更改横轴间距
docker — 容器存储_docker 保存容器-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读2.2k次。①Storage driver 处理各镜像层及容器层的处理细节,实现了多层数据的堆叠,为用户 提供了多层数据合并后的统一视图②所有 Storage driver 都使用可堆叠图像层和写时复制(CoW)策略③docker info 命令可查看当系统上的 storage driver主要用于测试目的,不建议用于生成环境。_docker 保存容器
随便推点
网络拓扑结构_网络拓扑csdn-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读834次,点赞27次,收藏13次。网络拓扑结构是指计算机网络中各组件(如计算机、服务器、打印机、路由器、交换机等设备)及其连接线路在物理布局或逻辑构型上的排列形式。这种布局不仅描述了设备间的实际物理连接方式,也决定了数据在网络中流动的路径和方式。不同的网络拓扑结构影响着网络的性能、可靠性、可扩展性及管理维护的难易程度。_网络拓扑csdn
JS重写Date函数,兼容IOS系统_date.prototype 将所有 ios-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读1.8k次,点赞5次,收藏8次。IOS系统Date的坑要创建一个指定时间的new Date对象时,通常的做法是:new Date("2020-09-21 11:11:00")这行代码在 PC 端和安卓端都是正常的,而在 iOS 端则会提示 Invalid Date 无效日期。在IOS年月日中间的横岗许换成斜杠,也就是new Date("2020/09/21 11:11:00")通常为了兼容IOS的这个坑,需要做一些额外的特殊处理,笔者在开发的时候经常会忘了兼容IOS系统。所以就想试着重写Date函数,一劳永逸,避免每次ne_date.prototype 将所有 ios
如何将EXCEL表导入plsql数据库中-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读5.3k次。方法一:用PLSQL Developer工具。 1 在PLSQL Developer的sql window里输入select * from test for update; 2 按F8执行 3 打开锁, 再按一下加号. 鼠标点到第一列的列头,使全列成选中状态,然后粘贴,最后commit提交即可。(前提..._excel导入pl/sql
Git常用命令速查手册-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读83次。Git常用命令速查手册1、初始化仓库git init2、将文件添加到仓库git add 文件名 # 将工作区的某个文件添加到暂存区 git add -u # 添加所有被tracked文件中被修改或删除的文件信息到暂存区,不处理untracked的文件git add -A # 添加所有被tracked文件中被修改或删除的文件信息到暂存区,包括untracked的文件...
分享119个ASP.NET源码总有一个是你想要的_千博二手车源码v2023 build 1120-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读202次。分享119个ASP.NET源码总有一个是你想要的_千博二手车源码v2023 build 1120
【C++缺省函数】 空类默认产生的6个类成员函数_空类默认产生哪些类成员函数-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读1.8k次。版权声明:转载请注明出处 http://blog.csdn.net/irean_lau。目录(?)[+]1、缺省构造函数。2、缺省拷贝构造函数。3、 缺省析构函数。4、缺省赋值运算符。5、缺省取址运算符。6、 缺省取址运算符 const。[cpp] view plain copy_空类默认产生哪些类成员函数