python可以小程序开发吗,python能开发应用程序吗-程序员宅基地
技术标签: 人工智能
大家好,给大家分享一下python可以用来开发小程序吗,很多人还不知道这一点。下面详细解释一下。现在让我们来看看!

用python做一个简单软件
前言
这是一个课设,用python做一个扫描王软件
我主要做的GUI部分,记录分享一下。也是第一次用python做小软件,python的方便果然是名不虚传
遇到问题
1.python版本
下载了python3.7的编译器
由于最终软件要在win7上运行,即32位的,因此下载了python3.7的32位
打包后遇到问题:w10打包的不能在w7上运行----->下载python32位的解释器
在w10执行python代码,参考博客: https://blog.csdn.net/qq_27280237/article/details/84644900
2.opencv降级
参考博客: https://www.cnblogs.com/guobin-/p/10842486.html
3.安装打包软件pyinstaller
参考博客: https://blog.csdn.net/Nire_Yeyu/article/details/104683888/
https://blog.csdn.net/Nire_Yeyu/article/details/104683888/
https://www.cnblogs.com/xbblogs/p/9682708.html
##最终打包代码
pyinstaller -F -w -i 图片名.ico 文件名.py
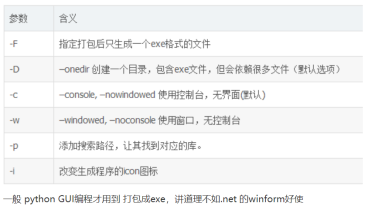
4.输出的图片没法保存
有中文路径
软件效果

python代码
1.GUI部分
import PySimpleGUI as sg
import PIL.Image
import scanner_doee2
import cv2
import os
import numpy as np
import other
from other import convert_to_bytes
from tkinter import *
# 全局变量
mp_path = ['读取图像','原图处理','滤镜']
mp_key = ['原图处理', '图像翻转', '寻找轮廓','读取图像','img0']
choices = ('素描滤镜','复古滤镜','反色滤镜','边界滤镜', '模糊滤镜','不加滤镜','浮雕滤镜')
#缓存图片标号
# 原图/翻转后的图片 0
# 圈出轮廓的图 10
# 透视变换后 11
# 调整亮度和对比度后的图 2
# 添加滤镜后的图 3
sg.theme('Light Blue 2')
layout1 = [
[sg.Frame(layout=[
[sg.Text('图像地址'), sg.Input(key='path_in'), sg.FileBrowse()],
[sg.Button('读取图像')]
], title='读图',title_color='blue')],
[sg.Button('翻转调整'),sg.Button('矫正处理')],
[sg.Frame(layout=[
[sg.Button('手动调节'), sg.Button('自适应均衡化'), sg.Button('清空效果')],
], title='亮度和对比度调节',title_color='blue')],
[sg.Frame(layout = [
[sg.Listbox(choices, size=(15, len(choices)), key='filter')],
[sg.Button('滤镜处理')]
], title='滤镜', title_color='blue') ],
[sg.Frame(layout=[
[sg.Button('阈值调节')]],
title='阈值', title_color='blue', relief=sg.RELIEF_SUNKEN, tooltip='Use these to set flags')],
[sg.Frame(layout=[
[sg.Radio('普通', "RADIO1",key='普通', default=True, size=(10, 1)), sg.Radio('拍书', "RADIO1",key='拍书'),sg.Radio('证书', "RADIO1", key='证件',default=False, size=(10, 1))]],
title='应用场景', title_color='blue', relief=sg.RELIEF_SUNKEN, tooltip='Use these to set flags')],
[sg.Frame(layout=[
[sg.Text('保存地址'), sg.Input(key='path_out'),sg.FolderBrowse(target='path_out')],
[sg.Button('输出图像')]
], title='输出',title_color='blue')],
]
layout2 = [[sg.Text('原图:')],
[sg.Image(key='img0',size=(300,300))],
[sg.Text('寻找到轮廓后的图:')],
[sg.Image(key='img10', size=(300, 300))],
[sg.Text('位置矫正+裁剪后的图:')],
[sg.Image(key='img11',size=(300, 300))]
]
layout3=[ [sg.Text('调整后的图')],
[sg.Image(key='img2',size=(500,500))]
]
layout = [[sg.Column(layout1, element_justification='c'), sg.VSeperator(),sg.Column(layout2, element_justification='c'),sg.Column(layout3, element_justification='c')]]
window = sg.Window('扫描王', layout)
while (True):
event, values = window.read()
if event !=None:
print(event,values)
if event =='读取图像':
path_in = values['path_in']
path_save=os.path.dirname(path_in)
img0=cv2.imread(path_in)
print(path_save)
scanner_doee2.varible(path_save)
# orig = img0 #备份原图
# 重新设置图片的大小,以便对其进行处理:选择最佳维度,以便重要内容不会丢失
# img0 = cv2.resize(img0, (1500, 880))
cv2.imwrite(path_save+'/img0.jpg',img0)
window['img0'].update(data=convert_to_bytes(path_in, (300,300)))
if event =='翻转调整':
img0=np.rot90(img0)
cv2.imwrite(path_save + '/img0.jpg', img0)
window['img0'].update(data=convert_to_bytes(path_save+'/img0.jpg', (300, 300)))
if event=='矫正处理':
img1=scanner_doee2.solve(img0)
img2=img1
img3=img1
window['img10'].update(data=convert_to_bytes(path_save+'/img10.jpg', resize=(300,300)))
window['img11'].update(data=convert_to_bytes(path_save+'/img11.jpg', resize=(300,300)))
if event=='清空效果':
img2=img1
cv2.imwrite(path_save + '/img2.jpg', img2)
window['img2'].update(data=convert_to_bytes(path_save+'/img2.jpg', resize=(500,500)))
if event=='手动调节':
img2=scanner_doee2.light(img2)
cv2.imwrite(path_save + '/img2.jpg', img2)
window['img2'].update(data=convert_to_bytes(path_save+'/img2.jpg', resize=(500,500)))
if event=='自适应均衡化':
img2=scanner_doee2.autoEqualHistColor(img2)
cv2.imwrite(path_save + '/img2.jpg', img2)
window['img2'].update(data=convert_to_bytes(path_save+'/img2.jpg', resize=(500,500)))
if event=='滤镜处理':
img3=img2
ss=values['filter']
print(ss,ss[0])
if ss[0]=='复古滤镜':
img3 = scanner_doee2.mirror2(img2)
elif ss[0]=='素描滤镜':
print(ss)
img3 = scanner_doee2.mirror1(img2)
elif ss[0] == '反色滤镜':
print(ss)
img3 = scanner_doee2.mirror3(img2)
elif ss[0] == '边界滤镜':
img3 = scanner_doee2.mirror4(img2)
elif ss[0] == '浮雕滤镜':
img3 = scanner_doee2.mirror5(img2,1)
elif ss[0] == '模糊滤镜':
img3 = scanner_doee2.mirror5(img2,2)
elif ss[0]=='不加滤镜':
img3=img2
cv2.imwrite(path_save + '/img2.jpg', img3)
window['img2'].update(data=convert_to_bytes(path_save + '/img2.jpg', resize=(500, 500)))
if event=='阈值调节':
img4=img2
img4=scanner_doee2.yuzhi(img2)
cv2.imwrite(path_save + '/img2.jpg', img4)
window['img2'].update(data=convert_to_bytes(path_save + '/img2.jpg', resize=(500, 500)))
if event=='输出图像':
img5=cv2.imread(path_save + '/img2.jpg')
h,w,c=img5.shape
# A4 297*210mm
# B5 250*176
# 身份证 54*85.6
if values['拍书']==True:
scale = min(h/250, w/176)
img5=cv2.resize(img5,(int(176* scale), int(250* scale)))
elif values['证件']==True:
scale = min(h/54, w/85.6)
img5=cv2.resize(img5,(int(85.6* scale), int(54* scale)))
elif values['普通']==True:
img5 = cv2.imread(path_save + '/img2.jpg')
cv2.imshow('output',img5)
path_out=values['path_out']
cv2.imwrite( path_out+ '/out.jpg', img5)
# cv2.imwrite(path_save + '/img2.jpg', img5)
if event == sg.WIN_CLOSED or event == 'Exit':
break
2.算法部分
import cv2
import numpy as np
from math import sqrt
import cmath
from PIL import Image, ImageFilter
path_save='yes'
def varible(ss):
global path_save
path_save=ss
print(path_save)
def rectify(h):
h = h.reshape((4,2)) #改变数组的形状,变成4*2形状的数组
hnew = np.zeros((4,2), dtype = np.float32) #创建一个4*2的零矩阵
#确定检测文档的四个顶点
add = h.sum(1)
hnew[0] = h[np.argmin(add)] #argmin()函数是返回最大数的索引
hnew[2] = h[np.argmax(add)]
diff = np.diff(h, axis = 1) #沿着制定轴计算第N维的离散差值
hnew[1] = h[np.argmin(diff)]
hnew[3] = h[np.argmax(diff)]
return hnew
# 拟合曲线顶点的去中心化
def approxCenter(approx):
sum_x,sum_y = 0,0
approx_center = approx;
for a in approx:
sum_x = sum_x + a[0][0];
sum_y = sum_y + a[0][1];
avr_x = sum_x/len(approx);
avr_y = sum_y/len(approx);
for a in approx_center:
a[0][0] = a[0][0] - avr_x
a[0][1] = a[0][1] - avr_y
return approx_center,avr_x,avr_y
#将顶点极坐标化,返回极角
def approxTheta(approx):
cn = complex(approx[0][0],approx[0][1]) #得到每个点相对中心的直角坐标
r,theta = cmath.polar(cn) #将直角坐标转为极坐标,得到极角
return theta
# 合并拟合多边形顶点中的相近点
# approx:拟合多边形(n维数组)
# M:距离阈值
def approxCombine(approx,M):
del_indexs = []
for i in range(len(approx)):
if i not in del_indexs: #判断是否是已删点,如果是则跳过计算
for j in range(i+1,len(approx)):
if j not in del_indexs: #判断是否是已删点,如果是则跳过计算
#计算两点距离
dis = sqrt((approx[i][0][0] - approx[j][0][0])**2 + (approx[i][0][1] - approx[j][0][1])**2)
if dis < M :
#将两个相近点,近似为中值点
approx[i][0][0] = (approx[i][0][0] + approx[j][0][0])/2
approx[i][0][1] = (approx[i][0][1] + approx[j][0][1])/2
del_indexs.append(j)
approx = np.delete(approx, del_indexs,0) #删除多余的近似点
approx,avr_x,avr_y = approxCenter(approx); #将顶点去中心化,用于计算极坐标
approx = sorted(approx, key = approxTheta, reverse = True) #按照极角进行降序排序
approx = np.array(approx) #sorted返回list型,转换为ndarray
# 恢复去中心的顶点
for a in approx:
a[0][0] = a[0][0] + avr_x
a[0][1] = a[0][1] + avr_y
return approx
#伽马变换
#gamma > 1时,图像对比度增强
def gamma_trans(input_image, gamma):
img_norm = input_image/255.0
img_gamma = np.power(img_norm,gamma)*255.0
img_gamma = img_gamma.astype(np.uint8)
return img_gamma
# 彩色直方图均衡(对比度增强)(效果一般)
def equalHistColor(img_in):
b, g, r = cv2.split(img_in)
b1 = cv2.equalizeHist(b)
g1 = cv2.equalizeHist(g)
r1 = cv2.equalizeHist(r)
img_out = cv2.merge([b1,g1,r1])
return img_out
# 彩色伽马变换(对比度增强)(效果较好)
def gammaColor(img_in,gamma):
b, g, r = cv2.split(img_in)
b1 = gamma_trans(b,gamma)
g1 = gamma_trans(g,gamma)
r1 = gamma_trans(r,gamma)
img_out = cv2.merge([b1,g1,r1])
return img_out
# 亮度调节,原理:将原图与一张全黑图像融合,调节融合的比例,即为亮度调节
# c为原图所占比例,c > 1时,亮度增强
def light_img(img1, c):
rows, cols, channels = img1.shape
# 新建全零(黑色)图片数组:np.zeros(img1.shape, dtype=uint8)
blank = np.zeros([rows, cols, channels], img1.dtype)
dst = cv2.addWeighted(img1, c, blank, 1-c, 0) #两幅图像融合,当1-c小于0时,亮度增强
return dst
def solve(image):
# print(path_save)
# path_save='C:/Users/53055/Desktop/pythonProject3'
#创建原始图像的副本
orig = image.copy()
orig_w, orig_h, ch = orig.shape # 读取大小
#重新设置图片的大小,以便对其进行处理:选择最佳维度,以便重要内容不会丢失
image = cv2.resize(image, (1500,880))
orig_h_ratio = orig_h / 1500.0 # 保存缩放比例
orig_w_ratio = orig_w / 880.0 # 保存缩放比例
#对图像进行灰度处理,并进而进行行高斯模糊处理
gray = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
blurred = cv2.GaussianBlur(gray, (5,5), 0)
#使用canny算法进行边缘检测
edged = cv2.Canny(blurred,0,50)
kernel = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_RECT, (2, 2))
edged = cv2.dilate(edged, kernel) # 膨胀
#创建canny算法处理后的副本
orig_edged = edged.copy()
#找到边缘图像中的轮廓,只保留最大的,并初始化屏幕轮廓
#findContours()函数用于从二值图像中查找轮廓
# RETR_LIST:寻找所有轮廓
# CHAIN_APPROX_NONE:输出轮廓上所有的连续点
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(edged, cv2.RETR_LIST, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE)
approxs = []
for c in contours:
p = cv2.arcLength(c, True) #计算封闭轮廓的周长或者曲线的长度
approx = cv2.approxPolyDP(c, 0.02*p, True) #指定0.02*p精度逼近多边形曲线,这种近似曲线为闭合曲线,因此参数closed为True
approx_cmb = approxCombine(approx,60) # 合并轮廓中相近的坐标点
if len(approx_cmb) == 4: #如果是四边
approxs.append(approx_cmb) #该轮廓为可能的目标轮廓
# 将轮廓的拟合多边型按面积大小降序排序
approxs = sorted(approxs, key = cv2.contourArea, reverse = True)
# 选取面积最大的四边形轮廓
target = approxs[0]
# 将轮廓映射到原图上
for t in target:
t[0][0] = t[0][0] * orig_h_ratio
t[0][1] = t[0][1] * orig_w_ratio
# 在原灰度图上绘制寻找到的目标四边形轮廓
orig_marked = orig
# all_approxs = cv2.cvtColor(temp, cv2.COLOR_GRAY2RGB)
cv2.drawContours(orig_marked,[target],-1,(0,255,0),8)
# cv2.imshow('orig_marked',orig_marked)
# 保存圈出轮廓的图
cv2.imwrite(path_save + '/img10.jpg', orig_marked)
# for i in range(len(approxs)):
# cv2.drawContours(all_approxs,[approxs[i]],-1,(0,255,0),2)
#将目标轮廓映射到800*800四边形(用于透视变换)
approx = rectify(target)
pts2 = np.float32([[0,0],[800,0],[800,800],[0,800]])
# 透视变换
# 使用gtePerspectiveTransform函数获得透视变换矩阵:approx是源图像中四边形的4个定点集合位置;pts2是目标图像的4个定点集合位置
M = cv2.getPerspectiveTransform(approx, pts2)
# 使用warpPerspective函数对源图像进行透视变换,输出图像dst大小为800*800
dst = cv2.warpPerspective(orig, M, (800,800))
# 进行位置校正、裁剪(透视变换)后的图像
# cv2.imshow("trans",dst)
cv2.imwrite(path_save + '/img11.jpg', dst)
return dst
# 彩色限制对比度自适应直方图均衡化(图像亮度均衡)
def autoEqualHistColor(img_in):
b, g, r = cv2.split(img_in)
clahe = cv2.createCLAHE(1,tileGridSize = (8,8))
b1 = clahe.apply(b)
g1 = clahe.apply(g)
r1 = clahe.apply(r)
img_out = cv2.merge([b1,g1,r1])
return img_out
# 手动调节亮度和对比度
def light(dst):
data=[110,220]
def l_c_regulate(x):
l = cv2.getTrackbarPos('light', 'light & contrast regulate')
gamma = cv2.getTrackbarPos('contrast', 'light & contrast regulate')
lighted = light_img(img_lc_regulate, l / 100.0) # 亮度调节
gammaed = gammaColor(lighted, gamma / 100.0) # gamma变换
cv2.imshow("light & contrast regulate", gammaed)
data=[l,gamma]
return gammaed
img_lc_regulate = dst # 复制原图
cv2.namedWindow('light & contrast regulate') #创建window
cv2.createTrackbar('light', 'light & contrast regulate', 110, 500, l_c_regulate) #亮度滑动条
cv2.createTrackbar('contrast', 'light & contrast regulate', 210, 500, l_c_regulate) #对比度滑动条
l_c_regulate(0) #先运行一次回调函数
while(1):
k=cv2.waitKey(1)&0xFF
if k==27: #ECS键
cv2.destroyWindow('light & contrast regulate')
lighted = light_img(img_lc_regulate, data[0] / 100.0) # 亮度调节
gammaed = gammaColor(lighted, data[1] / 100.0) # gamma变换
break
return gammaed
# 素描滤镜
def mirror1(img_in):
img_in = cv2.cvtColor(img_in, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) # 转为灰度图
img_in = cv2.equalizeHist(img_in) # 直方图均衡化
inv = 255- img_in # 图像取反
blur = cv2.GaussianBlur(inv, ksize=(5, 5), sigmaX=50, sigmaY=50) # 高斯滤波
res = cv2.divide(img_in, 255- blur, scale= 255) #颜色减淡混合
res = gamma_trans(res,2) #伽马变换,增强对比度
return res
#复古滤镜(运行超级慢)
def mirror2(img_in):
img_in = cv2.cvtColor(img_in, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) # 转为灰度图
im_color = cv2.applyColorMap(img_in, cv2.COLORMAP_PINK)
return im_color
# 反色滤镜
def mirror3(img_in):
inv = 255- img_in # 图像取反
return inv
# 边界滤镜(利用canny算子实现)
def mirror4(img_in):
img_in = cv2.cvtColor(img_in, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
img_f = cv2.Canny(img_in,100,200)
return img_f
# cv2.imshow('img_f',img_f)
def mirror5(dst,type):
img_f = Image.fromarray(cv2.cvtColor(dst,cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
if type ==1:
img_f = img_f.filter(ImageFilter.EMBOSS) #浮雕滤镜
elif type==2:
img_f = img_f.filter(ImageFilter.BLUR) #模糊滤镜
img_f = cv2.cvtColor(np.asarray(img_f),cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
return img_f
# # 以下为PIL库的部分滤镜效果
#
# # OpenCV的图片格式转换成PIL.Image格式
# img_f = Image.fromarray(cv2.cvtColor(dst,cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
#
# # 滤镜处理
# # ImageFilter.BLUR 模糊滤镜
# # ImageFilter.SHARPEN 锐化滤镜
# # ImageFilter.SMOOTH 平滑滤镜
# # ImageFilter.SMOOTH_MORE 平滑滤镜(阀值更大)
# # ImageFilter.EMBOSS 浮雕滤镜
# # ImageFilter.FIND_EDGES 边界滤镜
# # ImageFilter.EDGE_ENHANCE 边界加强
# # ImageFilter.EDGE_ENHANCE_MORE 边界加强(阀值更大)
# # ImageFilter.CONTOUR 轮廓滤镜
# img_f = img_f.filter(ImageFilter.EMBOSS) #浮雕滤镜
# # img_f = img_f.filter(ImageFilter.CONTOUR) #素描滤镜
# # img_f = img_f.filter(ImageFilter.FIND_EDGES) #边界滤镜
#
# # PIL.Image转换成OpenCV格式
# img_f = cv2.cvtColor(np.asarray(img_f),cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
def yuzhi(img_in):
# 二值化阈值调节示例
# 关于二值化,用身份证照片测试时,全局阈值进行二值化效果还可以,但如果存在灰度不均匀,会出现部分信息缺失
# OTSU自动阈值法的效果也不错(效果不错的前提是图像灰度均匀,本质是一种全局最佳阈值的方法,依旧存在全局阈值的缺点)
# 使用区域自适应阈值时,对不同灰度的区域有很好的效果,但如果窗口过小,会导致噪点被放大,可以通过调节偏移阈值去除噪点
# 窗口调大到一定值时,效果等同于使用全局阈值,因此最终使用区域自适应阈值方法进行二值化
# demo中使用滑块调节自适应阈值窗口的size,
# 关于消除噪点,尝试过高斯滤波、膨胀,效果不好
data=[57,30]
def bin_regulate(x):
data[0] = cv2.getTrackbarPos('auto size', 'bin regulate') # 自适应阈值窗口大小
if data[0] == 0:
data[0] = 1 # 窗口最小大小为3
data[1] = cv2.getTrackbarPos('threshold', 'bin regulate') # 自适应阈值偏移量
# img_bin = cv2.GaussianBlur(img_bin, ksize=(3, 3), sigmaX=100, sigmaY=100) #高斯滤波
# 固定全局阈值二值化
# ret,img_bin = cv2.threshold(img_bin, t, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
# OTSU自动阈值
# ret,img_bin = cv2.threshold(img_bin, 0, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY+cv2.THRESH_OTSU)
# 以下两种区域自适应阈值方法类似
# 自适应阈值二值化(均值):第二个参数为领域内均值,第五个参数为规定正方形领域大小(11*11),第六个参数是常数C:阈值等于均值减去这个常数
# img_bin = cv2.adaptiveThreshold(img_bin, 255, cv2.ADAPTIVE_THRESH_MEAN_C, cv2.THRESH_BINARY, 21, 2)
# 自适应阈值二值化(高斯窗口)第二个参数为领域内像素点加权和,权重为一个高斯窗口,第五个参数为规定正方形领域大小(11*11),第六个参数是常数C:阈值等于加权值减去这个常数
img_bin = cv2.adaptiveThreshold(img_bin_i, 255, cv2.ADAPTIVE_THRESH_GAUSSIAN_C, cv2.THRESH_BINARY, 2 * data[0] + 1, data[1])
# 膨胀
# kernel = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_RECT, (3, 3))
# img_bin = cv2.dilate(img_bin,kernel) #膨胀
# 中值滤波
# img_bin = cv2.medianBlur(img_bin, 2*blur_size+1)
cv2.imshow("bin regulate", img_bin)
pass
img_gray = cv2.cvtColor(img_in, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) # 转为灰度图
img_bin_i = img_gray # 复制灰度图
cv2.namedWindow('bin regulate') # 创建window
cv2.createTrackbar('auto size', 'bin regulate', 57, 400, bin_regulate) # 自适应阈值的窗口size值
cv2.createTrackbar('threshold', 'bin regulate', 30, 100, bin_regulate) # 自适应阈值偏移量
bin_regulate(0) # 先运行一次回调函数
while (1):
k = cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF
if k == 27: # ECS键
img_bin = cv2.adaptiveThreshold(img_bin_i, 255, cv2.ADAPTIVE_THRESH_GAUSSIAN_C, cv2.THRESH_BINARY,
2 * data[0] + 1, data[1])
cv2.destroyWindow('bin regulate')
break
return img_bin
# while (1):
# k = cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF
#
# if k == 27: # ECS键
# cv2.destroyWindow('light & contrast regulate')
# img_bin = cv2.adaptiveThreshold(img_bin_i, 255, cv2.ADAPTIVE_THRESH_GAUSSIAN_C, cv2.THRESH_BINARY,
# 2 * data[0] + 1, data[1])
# break
return img_bin
def other():
# 二值化
# 对透视变换后的图像进行灰度处理
img_gray = cv2.cvtColor(dst, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
img_gray = gamma_trans(img_gray,1.2) #伽马变换,增强对比度
# 二值化阈值调节示例
# 关于这个二值化,用身份证照片测试时,全局阈值进行二值化效果还可以,但如果存在灰度不均匀,会出现部分信息缺失
# 使用区域自适应阈值时,对不同灰度的区域有很好的效果,但如果窗口过小,会有很多噪点被放大
# 窗口调大到一定值时,效果等同于使用全局阈值,因此最终使用区域自适应阈值方法进行二值化
# demo中使用滑块调节自适应阈值窗口的size
# 为了消除噪点,尝试过高斯滤波、膨胀,效果不好
# OTSU自动阈值法的效果也不错(效果不错的前提是图像灰度均匀,本质是一种全局最佳阈值的方法,依旧存在全局阈值的缺点)
def bin_regulate(x):
t = cv2.getTrackbarPos('auto size', 'bin regulate')
if t == 0:
t = 1 # 窗口最小大小为3
# blur_size = cv2.getTrackbarPos('blursize', 'bin regulate')
# img_bin = cv2.GaussianBlur(img_bin_regulate, ksize=(3, 3), sigmaX=100, sigmaY=100) #高斯滤波
# ret,img_bin = cv2.threshold(img_bin_regulate, t, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY) #进行固定阈值处理,得到二值图像
img_bin = img_bin_regulate
# 以下两种自适应阈值方法类似
# 自适应阈值二值化(均值):第二个参数为领域内均值,第五个参数为规定正方形领域大小(11*11),第六个参数是常数C:阈值等于均值减去这个常数
# img_bin = cv2.adaptiveThreshold(img_bin, 255, cv2.ADAPTIVE_THRESH_MEAN_C, cv2.THRESH_BINARY, 21, 2)
# 自适应阈值二值化(高斯窗口)第二个参数为领域内像素点加权和,权重为一个高斯窗口,第五个参数为规定正方形领域大小(11*11),第六个参数是常数C:阈值等于加权值减去这个常数
img_bin = cv2.adaptiveThreshold(img_bin,255, cv2.ADAPTIVE_THRESH_GAUSSIAN_C, cv2.THRESH_BINARY, 2*t+1, 2)
# OTSU自动阈值(效果还可以)
# ret,img_bin = cv2.threshold(img_bin, 0, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY+cv2.THRESH_OTSU)
# 膨胀
# kernel = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_RECT, (3, 3))
# img_bin = cv2.dilate(img_bin,kernel) #膨胀
cv2.imshow("bin regulate",img_bin)
pass
img_bin_regulate = img_gray #复制灰度图
cv2.namedWindow('bin regulate') #创建window
cv2.createTrackbar('auto size', 'bin regulate', 1, 400, bin_regulate) #自适应阈值的窗口size值
# cv2.createTrackbar('blursize', 'bin regulate', 1, 100, bin_regulate) #高斯滤波size滚动条
bin_regulate(0) #先运行一次回调函数
# #对透视变换后的图像使用阈值进行约束获得扫描结果
# # 使用固定阈值操作:threshold()函数:有四个参数:第一个是原图像,第二个是进行分类的阈值,第三个是高于(低于)阈值时赋予的新值,
# # 第四个是一个方法选择参数:cv2.THRESH_BINARY(黑白二值)
# # 该函数返回值有两个参数,第一个是retVal(得到的阈值值(在OTSU会用到)),第二个是阈值化后的图像
# ret, th1 = cv2.threshold(dst, 132, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY) #进行固定阈值处理,得到二值图像
# # 使用Otsu's二值化,在最后一个参数加上cv2.THRESH_OTSU
# ret2, th2 = cv2.threshold(dst, 0, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY+cv2.THRESH_OTSU)
# # 使用自适应阈值操作:adaptiveThreshold()函数
# # 第二个参数为领域内均值,第五个参数为规定正方形领域大小(11*11),第六个参数是常数C:阈值等于均值减去这个常数
# th3 = cv2.adaptiveThreshold(dst, 255, cv2.ADAPTIVE_THRESH_MEAN_C, cv2.THRESH_BINARY, 11, 2)
# # 第二个参数为领域内像素点加权和,权重为一个高斯窗口,第五个参数为规定正方形领域大小(11*11),第六个参数是常数C:阈值等于加权值减去这个常数
# th4 = cv2.adaptiveThreshold(dst,255, cv2.ADAPTIVE_THRESH_GAUSSIAN_C, cv2.THRESH_BINARY, 11, 2)
#输出处理后的图像
cv2.imshow("orig", orig)
cv2.imshow("gray", gray)
cv2.imshow("blurred", blurred)
cv2.imshow("canny_edge", orig_edged)
cv2.imshow("marked", image)
# cv2.imshow("thre_constant", th1)
# cv2.imshow("thre_ostu", th2)
# cv2.imshow("thre_auto1", th3)
# cv2.imshow("thre_auto2", th4)
cv2.imshow("orig_mark", dst)
# cv2.imwrite("orig.jpg",dst)
# cv2.imshow('all-approxs',all_approxs)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
3.辅助代码
import PIL.Image
import io
import base64
global filename
def convert_to_bytes(file_or_bytes, resize=None):
'''
Will convert into bytes and optionally resize an image that is a file or a base64 bytes object.
Turns into PNG format in the process so that can be displayed by tkinter
:param file_or_bytes: either a string filename or a bytes base64 image object
:type file_or_bytes: (Union[str, bytes])
:param resize: optional new size
:type resize: (Tuple[int, int] or None)
:return: (bytes) a byte-string object
:rtype: (bytes)
'''
if isinstance(file_or_bytes, str):
img = PIL.Image.open(file_or_bytes)
else:
try:
img = PIL.Image.open(io.BytesIO(base64.b64decode(file_or_bytes)))
except Exception as e:
dataBytesIO = io.BytesIO(file_or_bytes)
img = PIL.Image.open(dataBytesIO)
cur_width, cur_height = img.size
if resize:
new_width, new_height = resize
scale = min(new_height/cur_height, new_width/cur_width)
img = img.resize((int(cur_width*scale), int(cur_height*scale)), PIL.Image.ANTIALIAS)
bio = io.BytesIO()
img.save(bio, format="PNG")
del img
return bio.getvalue()
def save_pic(filename,type,id):
mp_type = {'0': '原图翻转', '白元芳': 78, '狄仁杰': 82}
智能推荐
重生奇迹mu武器镶嵌顺序-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读71次。例如:雷1J10%冰技能+37火每等级,这样就可以30%出现属性,如果没有出,可以破坏某一个洞,继续镶嵌同属性的宝石,直到定现为止,由于1J雷和37技能冰的比较贵,所以可以破坏火荧石,不断镶嵌到出现属性为止。荧光宝石可从以前的物品中获得。从上到下的镶嵌顺寻按照雷、冰、火镶嵌,就有30%的概率出现技能攻击力加11的幸运荧光属性。从上到下的镶嵌顺寻按照土、风、水镶嵌,就有30%的概率出现最大生命值+29的幸运荧光属性。从上到下的镶嵌顺寻按照火、冰、雷镶嵌,就有30%的概率出现攻击力加11的幸运荧光属性。
人工智能第三章(1)——无信息搜索(盲目搜索) (附书本资料)_无信息搜索又称为-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读8.8k次,点赞21次,收藏51次。这篇文章的意义在于哪里呢?1)向大家展示如何形式化定义一个搜索问题,又如何去求解;2)通过讲述各种盲目搜索算法,帮大家梳理无信息搜索的脉络。_无信息搜索又称为
【图像重建】基于小波变换结合BP、OMP、StOMP实现图像重建含MSE PSNR附Matlab代码-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读847次,点赞18次,收藏20次。图像重建是数字信号处理领域的一个重要问题,它涉及到从损坏或不完整的图像数据中恢复出高质量的图像。在图像重建的研究中,小波变换结合各种重建算法已经成为一个热门的研究方向。本文将介绍基于小波变换结合BP、OMP、StOMP算法实现图像重建,并对重建效果进行评估,包括均方误差(MSE)和峰值信噪比(PSNR)。小波变换是一种多尺度分析方法,它可以将信号分解成不同尺度的频率成分,从而更好地捕捉信号的局部特征。在图像重建中,小波变换可以将图像分解成不同尺度的小波系数,然后利用这些小波系数进行重建。
指针数组 数组指针 的判断_int*做参数如何判断是整型还是数组-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读685次。用变量a给出下面的定义:一个有10个指针的数组,该指针指向一个函数,该函数有一个整形参数并返回一个整型数*int a[10];这是一个指针数组。数组a里存放的是10个int型指针*int (a)[10];这是一个数组指针。a是指针,指向一个数组。数组a有10个int型元素。*int (a)(int);这个表示一个内存空间,这个空间用来存放一个指针,这个指针指向一个函数,这个函数有一个类..._int*做参数如何判断是整型还是数组
Linux运维常用命令和正则表达式_linux cp命令加正则表达式-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读1k次。1.删除0字节文件find -type f -size 0 -exec rm -rf {} ;2.查看进程按内存从大到小排列ps -e -o “%C : %p : %z : %a”|sort -k5 -nr3.按cpu利用率从大到小排列ps -e -o “%C : %p : %z : %a”|sort -nr4.打印说cache里的URL_linux cp命令加正则表达式
rsa算法 c#语言,C#实现简单的RSA非对称加密算法示例-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读639次。本文实例讲述了C#实现简单的RSA非对称加密算法。分享给大家供大家参考,具体如下:界面控件namespace RSA算法{partial class Form1{/// /// 必需的设计器变量。/// private System.ComponentModel.IContainer components = null;/// /// 清理所有正在使用的资源。/// /// 如果应释放托管资源,为..._c# 非对称加密算法
随便推点
夏天到,装饰器让Python秀出性感属性:Property+Decorators+-+Getters,+Setters,+and+Deleters_@property (decorators)-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读262次。John Smith曾经是我的好基友,没有之一,今天我们拿他做个试验:初始代码,我们做一个打印员工John Smith信息的类,实例emp_1会用类属性输出:class Employee: def __init__(self, first, last): self.first = first self.last = last self.email = first + "." + last + '@email.com' def fullnam_@property (decorators)
Oracle单个字段多记录拼接_oracle 一个字段多条记录的拼接-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读2.4k次。sql查询中,一个字段多个结果拼接的两种方式_oracle 一个字段多条记录的拼接
vue 项目中 html中出现clear错误_[vue/comment-directive] clear-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读934次。clear报错_[vue/comment-directive] clear
科大讯飞离线关键词识别(语法识别)(2)_科大讯飞构建语法树-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读2.7k次。关键词识别和语音听写还是有差别的,语音听写是直接将所说的话转化成语音,至于识别的准确率看所说的话是否是常用的,如果遇到不常见的词比如背身腿降这个指令,识别出来的就是乱七八糟的。而关键词识别也就是针对这种关键词识别有很好的效果,在于你自己构建一个.bnf文件,然后写上关键词#BNF+IAT 1.0 UTF-8;!grammar call;!slot <contact>;!slo..._科大讯飞构建语法树
DeepCache:Principled Cache for Mobile Deep Vision (MobiCom2018)-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读701次。提示:文章写完后,目录可以自动生成,如何生成可参考右边的帮助文档文章目录DeepCache:Principled Cache for Mobile Deep Vision (MobiCom2018)一、摘要二、缓存的思想和挑战1. 缓存思想的引入1) CNN是视频处理的常用算法,但在资源有限的设备端受限2) 如何解决设备端受限这一问题——缓存2. 挑战1) 缓存中的可重用结果查找2) CNN中间特征图的细粒度重用3) 平衡可缓存性、模型准确性和高速缓存开销4) 对抗缓存侵蚀(cache erosion._deepcache
Manjaro-Linux感觉蛮有用的系统问题处理-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读201次。添加国内软件源导入GPG Keyoh-my-zsh 安装配置出现Keys错误,签名之类的问题安装编译环境出现无法锁定database的错误的解决办法蓝牙耳机连接上了但是不能听到声音的问题Manjaro Gnome桌面在集成显卡下动画卡顿的问题Manjaro 默认终端gnome-terminal不能设置透明背景的问题使用ibus输入法打字卡顿的问题Stea..._manjaro ficitx